GExplore User Guide
Welcome to GExplore. The help pages are arranged to help a new user navigate this website. Experienced users can jump directly to the FAQ section.
- The introduction part provides background information.
- The Databases section explains the content of the GExplore databases.
- The Search fields section explains what is behind the search fields, some of which allow complex searches.
- When you hit the 'search' button you will be presented with a result page that allows you to further explore the data related to genes that fulfilled your search conditions. Those are covered under the 'Display option' section.
- The 'Tools' part contains two simple features that can help you to continue with the genes you found outside of GExplore.
- The FAQ section might address some questions that come up, when you use the website.
Last updated on Oct 14, 2024
Introduction
Overview
GExplore is a tool designed to offer quick access to data related to gene or protein function in C. elegans. The interface is simple, and response times are fast to encourage exploratory searches with a large number of genes.
The database contains selected genome-wide data sets, including protein domain organization, gene expression, and phenotype data, which are important indicators for gene and protein function. Data sets were obtained from WormBase and selected original research papers and processed to integrate data and to simplify searches.
This site should be useful for experimental planning of genome-scale experiments quick and survey-type queries. With this interface, you should be able to get quick answers to questions such as:
- How many small secreted proteins are there?
- Which putative cell surface receptors are expressed in neurons?
- How many kinases expressed in muscle cells have putative null alleles available?
Users can also enter their own lists of genes (up to several thousand) and extract subets of genes with certain characteristics.
What's new?
The latest version of GExplore (1.5, October 2024) is a major update including updates to the gene, mutation and protein databases as well as novel data sets and features. The web interface was completely redesigned
Database update
- Gene and mutation databases were updated to WormBase release WS294.
- The Gene database now contains disease associations, interacting genes and expression data from 'genomic studies' for text searches.
- Display functions for the mutation database were expanded to show the breakpoints of deletions and whether the deletion causes a frameshift or not.
- The protein database now contains proteome and ortholog data from 19 nematodes species and five 'model organsims'.
- GExplore now hosts three genome-wide published RNA-seq data sets:
- stages: expression profiles from 18 different embryonic and larval stages; see Boeck, M et al., (2016).
- tissues: expression profiles for 27 tissues and cell types at the L2 larval stage; see Cao et al. (2017).
- embryo: expression profiles for seven embryonic cell populations from gastrulation to terminal differentiation; see Warner et al. (2019).)
Website redesign
- All webpages were redesigned to make the site more accessible for novel users
- The help pages were reorganized and expanded.
- The search pages have short help text to show what the purpose of the various search fields.
- The result pages have a side bar with sections for search results data, display and download options as well as a help section.
Latest news
March 2025
A new RNAseq database was added. It contains data from several hundred embryonic cells at different stages in C. elegans and C. briggsae.
May 2025
The gene and mutation databases have been updated to Wormbase release WS296.
Last updated on May 12, 2025
Databases
GExplore consists of six different databases, each with its own search page.
Genes
The gene database contains curated datasets relevant to predict the putative function(s) of genes and proteins. These datasets are:
- Protein domain organization
- General gene description
- Phenotype and expression data
- Gene interaction data
- Gene ontology (GO) terms
- Disease associations
In addition the database contains the genetic/nucleotide position of the genes allowing the user to select/identify all genes in a particular region of a chromosome. All data have been sourced from WormBase. The current version is based on WormBase release 294 (October 2024).
The search interface allows users to quickly identify groups of genes that share specific features, such as genes associated with Parkinson's Disease that are expressed in dopaminergic neurons. Alternatively, users can input large lists (hundreds or thousands) of candidate genes and filter them based on certain characteristics.
The database contains all splice variants of a gene. However, gene-specific data such as description, expression, phenotype etc are only associated with the 'longest splice variant'. The other splice variants will have "N/A" in the corresponding columns. This means the database does not contains any splice-variant specific data. This includes the 'nucleotide position'.
The system’s fast response time and flexible output options make it easy to perform efficient, survey-type queries with large groups of genes in both the input and output.
Mutations
Mutation data were downloaded from WormBase release 294 (October 2024). The dataset includes only exonic alleles and alleles affecting splice junctions, while SNPs from wildtype isolates have been excluded. This curated list of mutations is enriched for alleles likely to affect protein function.
The location of the mutations is mapped onto the domain organization of the protein, providing a visual display of both the location and nature of the mutations. For deletions, a color code is used to distinguish between in-frame deletions (purple) and frameshift deletions (red). The deletion endpoints are indicated as being located either 'outside' the gene, in an 'intron', or in an 'exon'. Display options also include the ability to show the protein sequence with the affected amino acids highlighted. Mutations are mapped to all known splice variants of the gene, enabling easy identification of alleles specific for a particular splice variant.
The WS296 version of the database contains:
- 226,242 alleles in 19,661 genes (28,247 splice variants)
- 13,018 deletions
- 183,564 missense alleles
- 10,016 nonsense alleles
- An additional 8,818 alleles without molecular information.
These are mostly older alleles where the molecular information was never entered in WormBase.
Proteins
The protein database contains data from 13 Caenorhabditis species (C. becei, C. brenneri, C. briggsae, C. elegans, C. japonica, C. parvicauda, C. quiockensis, C. remanei, C. sulstoni, C. uteleia, C. tropicalis, C. waitukubuli, C. zanzibari), representing all branches of the Caenorhabditis phylogenetic tree.
In addition, the database contains proteome data from 7 other nematode species (B. malayi, O. tipulae, O. volvulus, P. pacificus, P. redivivus, S. ratti, T. muris) that have high-quality data available. For comparison, the database also includes the proteomes of major model organisms (S. cerevisiae, D. melanogaster, D. rerio, M. musculus, H. sapiens).
Protein data were downloaded either from WormBase (for nematode species) or from the reference proteome site for model organisms. SMART was used for protein domain prediction.
To facilitate comparisons across species, the database also contains information about homologs in all species included in the database. The search interface allows users to select proteins with specific protein domains or domain arrangements for a chosen species. The output can be limited to proteins with homologs in one or more other species, enabling quick identification of either nematode-specific genes or evolutionarily conserved genes of a certain type (e.g. kinases).
Expressions
Expression (Stages)
The expression data for the different stages of the life cycle of C. elegans were obtained as part of the NHGRI modENCODE project, in collaboration with the Waterston (Max Boeck, Chau Huynh, LaDeana Hillier, University of Washington), Reinke (Guilin Wang, Dionna Kasper, Yale University), and Miller (Clay Spencer, Vanderbilt University) labs ( Hillier et al. (2009), Gerstein et al. (2010), Gerstein et al. (2014), Boeck et al. (2016)).
Briefly, 18 samples were analyzed using RNA-seq. The results provided here represent a subset of that data, derived from synchronized whole animals at embryonic and post-embryonic stages. For post-embryonic stages, two or more biological replicates were obtained, and weighted averages are provided. For embryonic stages, four independent time series were collected, with samples taken every 30 minutes (though some samples were lost due to technical failures). For detailed data collection and analysis, see Boeck et al. (2016).
Expression for each gene is provided in dcpm units (depth of coverage per million 35 base reads)1. This measure offers base-pair resolution, which simplifies the analysis of shorter features such as exons and splice junctions. A dcpm value of 1.5 represents an average expression level. Values between 0.003 and 0.1 generally indicate significant expression. To approximate rpkm values, use the following equation: rpkm = dcpm * 1000 / 35.
Expression (Tissues)
The expression data for cells and tissues at the L2 larval stage were generated using Single-cell Combinatorial Indexing RNA-seq (sci-RNA-seq). For details on data collection and analysis, see Cao et al. (2017). In brief, the expression profiles of nearly 50,000 cells from the L2 stage were determined using sci-RNA-seq. From this dataset, consensus expression profiles for 27 cell types were defined.
The profiles available through GExplore correspond to the data in Tables S2 to S4 of Cao et al. (2017), while images of the expression profiles align with Figure S14. Expression levels for each gene are presented in transcripts per million (TPM).
Enrichment data were pre-calculated and are presented as the "ratio" of a gene's expression in the most highly expressing cell type compared to the second-most highly expressing cell type. "qval" represents the false detection rate (FDR) at which the gene is considered differentially expressed between the highest and second-highest expressing cell types.
For reference, in Cao et al. (2017), a gene is labeled as "cell type enriched" if the ratio >= 5 and q-val < 0.05.
Expression (Embryo)
The expression data for embryonic tissues were generated using RNA-seq. For detailed information on data collection and analysis, see Warner et al. (2019). In brief, synchronized populations of embryos expressing tissue-specific fluorescent markers were sampled at 90-minute intervals over five time points, starting 120 minutes after embryo isolation (about halfway through gastrulation, referred to as t0).
The final time point (480 minutes after isolation, t4) corresponds to the early 3-fold stage, when cells begin terminal differentiation, but before cuticle formation. Time series data were collected for five different tissues/organs—hypodermis, intestine, pharynx, muscle, and neurons—as well as for two lineage-specific populations (ABa and ABala).
Expression levels are reported in transcripts per million (TPM).
Expression (species)
For detailed information on data collection and analysis, see Large et al. (2015). A link to a free electronic reprint is here. In brief, synchronized embryos, spanning the 28-cell stage to terminal differentiation were dissociated into single cells and sequenced for their RNA content using the 10X Genomics platform. The dataset contains >200,000 C. elegans and >190,000 C. briggsae cells that were labeled for their cellular identity using known molecular markers. The data presented here are summary expression values in Transcripts Per Million (TPM) for each cell type annotated in the dataset. Terminally differentiated cell types were further subdivided into time bins using an estimated ‘embryo time’ value that attempts to approximate when in development the single cell originates from. Single-cell RNA-sequencing allows for the capture of expression for individual cells across an animal. However, due to methodological inefficiencies, the expression values are frequently ‘zero-inflated’, meaning that expression values are often zero for a given gene in a single cell. Using many individual cells of a cell type, we can estimate the average expression value in a summary metric such as the transcripts per million (TPM). However, genes with expression on the lower end of the spectrum tend to still be inherently noisy. We caution on the over interpretation of TPM values below 80 for most cell types in these data.
Using the strategy of correlating our single-cell expression values with the bulk embryo time course results in poor estimations for the germline, as these cells frequently correlate with early embryonic expression (<28-cell stage) greater than any other timepoint. To circumvent this issue, we use a method called pseudo time estimation from the Monocle3 package (https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.2859). It tries to order cells along a developmental trajectory. We subdivided the germline into three pseudo time bins, ‘early’, ‘middle’ and ‘late’.
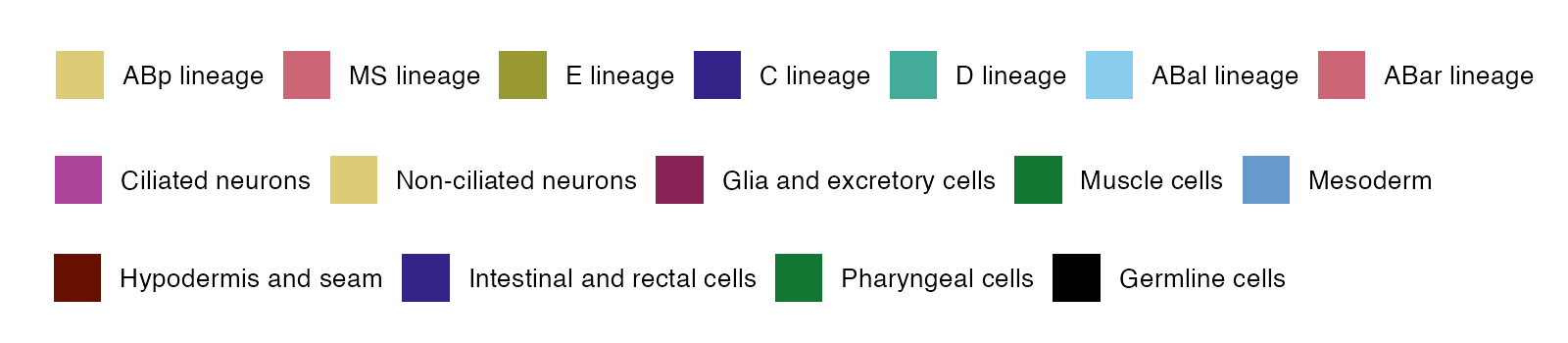
The database contains 615 data points (different cell types and/or different time points). Cells are grouped in the following way.
- ABp lineage (96 cells)
- ABal lineage (84 cells)
- ABar lineage (41 cells)
- MS lineage (53 cells)
- E lineage (2 cells)
- C lineage (22 cells)
- D lineage (4 cells)
- Ciliated neurons (20 cell types, 2-3 timepoints)
- Non-Ciliated neurons (47 cell types, 1-3 timepoints)
- Glia and excretory cells (10 cell types, 1-3 timepoints)
- Muscle cells (8 cell types, 3 timepoints)
- Mesoderm (8 cell types, 1-4 timepoints)
- Hypodermis and seam (9 cell types, 1-4 timepoints)
- Intestinal and rectal cells (6 cell types, 3-4 timepoints)
- Pharyngeal cells (16 cell types, 1-3 timepoints)
- Germline cells (3 timepoints)
The following color code is used in the expression graphs.
OrthoFinder2 was used to systematically group homologous C. elegans and C. briggsae genes into ‘orthogroups’ by reciprocal BLAST searches. On the display page the user has the option to display all members of the orthogroup(s) for a direct comparison of the expression of homologous genes in the two species.
Last updated on March 16, 2025
Search Fields
Overview
You only need to enter search terms in one of the search fields. If you enter search terms in multiple fields, they will be combined for an 'and' search (the result will contain only genes that fulfill all search criteria). You can hit the 'back' button on your broswer to go back to the search page to modify a search. When you start a completely new search, make sure that you clear the search fields. Any 'left-over' entries from previous search typically result in '0 genes found', since entires in all search fields are combined for an 'and' search.
What to expect?
Once the search is executed, the results will be displayed in table format. On the result page, you can:
- Select additional data to display.
- Remove genes from the result table to finetune the output
- Export the table as text or csv file.
Gene Search Field
The gene search field accepts the following identifiers (or any combination):
- WormBase gene ID:
WBGene00003738 - Gene sequence name:
F54F3.1 - Locus name:
nid-1 - Protein sequence name:
F54F3.1a
Names can be separated by commas, semicolons, space or newline characters. You can enter (or copy) a list of thousands of gene names for a single search. * can be used as a wildcard character, representing one or more characters of any kind. For example, unc-* means all gene names beginning with unc-.
Protein Domain Search Fields
Domain
Enter one or more of the domain abbreviations from the table of domain abbreviations (example: EGF, KIN) or SMART/Pfam identifiers (example: SM00273, PF12423). Domain abbreviations are case-sensitive! This field features autosuggest for domain abbreviations. Search terms are not limited to the suggested terms, i.e. you can ignore them. You can use * as wildcard character, e.g. 7TM* will find all domains beginning with 7TM* (7TM_GPCR_Sra, 7TM_GPCR_Srab, 7TM_GPCR_Srb, etc)
Domain Pattern
Use this field to search for proteins with certain domain combinations. Think of a protein as a linear sequence of domains like IG IG IG FN3 FN3 TM 324. You can use * as wildcard character representing 0 or more domains of any kind and numbers (but no Boolean terms) in the following way:
| Pattern Input | Description |
|---|---|
IG IG IG |
3 IGs in a row with no other domain in between. |
IG*FN3 |
The IG domain is eventually followed by an FN3 domain. |
3IG |
Expanded to IG IG IG: 3 IG domains in a row. Ensure there’s no space between the number and the domain abbreviation. |
3IG% |
Represents IG*IG*IG: 3 IGs with other domains interspersed (% acts as a wildcard during expansion). |
3-5IG |
Represents 3 to 5 IG domains: IG IG IG, IG IG IG IG, or IG IG IG IG IG. |
<3IG FN3 |
Translated as IG FN3 or IG IG FN3: meaning at least 1 but no more than 2 IGs followed by FN3. |
>3IG FN3 |
Translated as IG IG IG IG*FN3: meaning at least 4 IGs followed by FN3. |
Text Search Fields
General rules
The text search fields on the "Genes" search page are: Description, Phenotype, Expression, Gene Ontology, and Disease Association. All except for the 'description' text field use WormBase-defined vocabularies. This means the database only contains terms that are part of the corresponding vocabulary. To help the user identify, which terms can be used, these search fields offer autosuggest functionality. However, input is not limited to suggested terms. In any text search field you can use any term, e.g. searching for muscle will find any term containing muscle such as muscle_cell or vulval_muscle when used in the expression search field and spicule muscles of the male when used in the description text field.
Text search fields will return any match to the search term(s). You don't need to use * as wildcard character. You can ...
- ... use comma-separated lists for an OR Search
- ... use Boolean logic to combine search terms:
((axon and dendrite) or neuron) not muscle
| Search Type | Example | Result | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| AND Search | axon and dendrite |
Only results containing both "axon" and "dendrite". | Use when you want to narrow down results to items that meet all criteria. This gives fewer, more specific results. |
| OR Search | axon or dendrite |
Results containing either "axon", or "dendrite", or both. | Use when you want to broaden the search to include items that match any of the criteria, increasing the number of results. |
| NOT Search | neuron not muscle |
Results containing "neuron" but not "muscle". | Use when you want to limit the search to exclude items. |
On the output page, search terms for the text search fields will be highlighted for easier recognition.
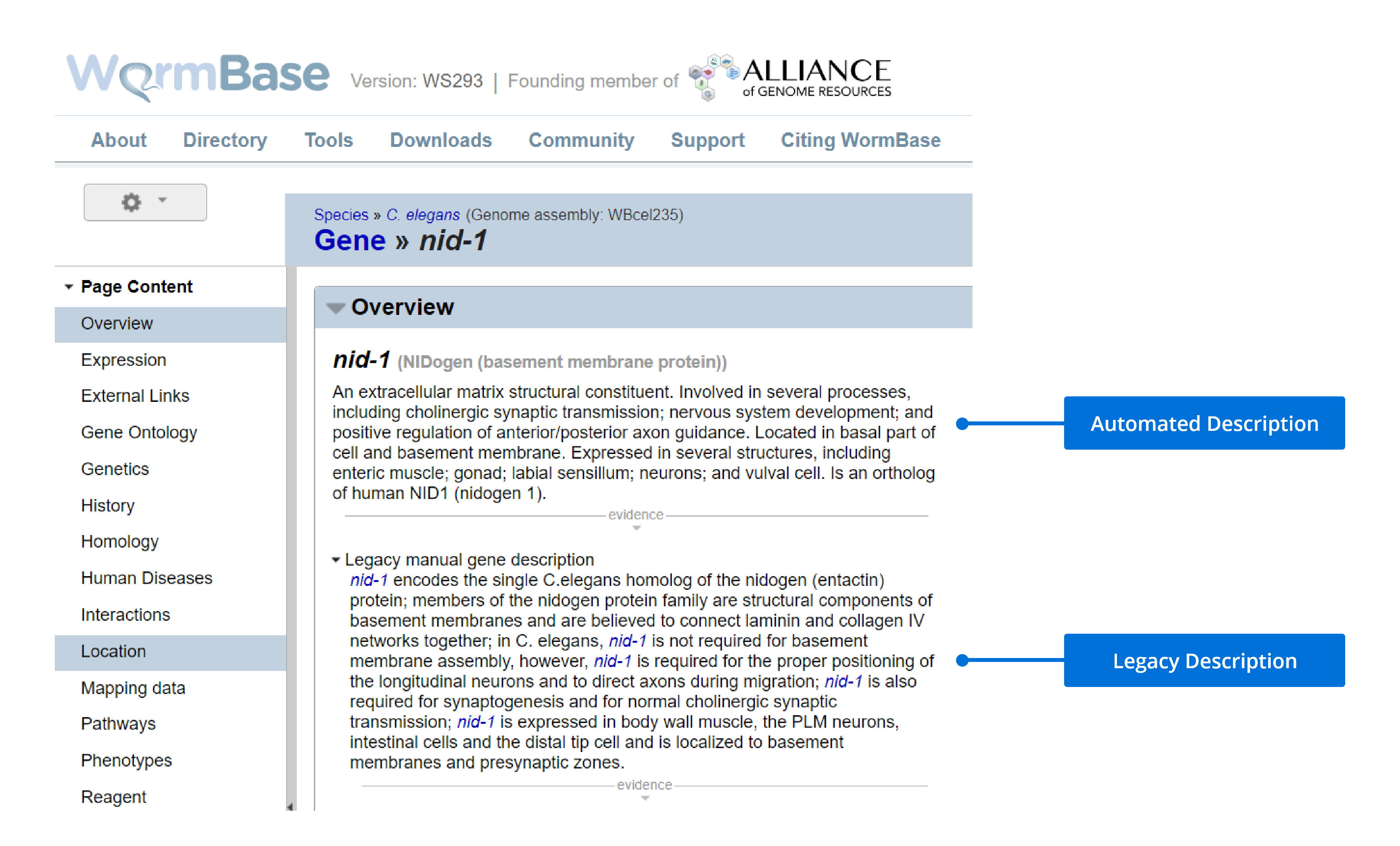
Description Search Field
The Legacy Description is equivalent to the "Legacy manual gene description" in WormBase, while the Automated Description is the top-level description under the “Overview” tab in WormBase.
Phenotype and Expression Search Fields
The Phenotype and Expression search fields use WormBase-defined vocabularies. These fields include an autosuggest function, which suggests search terms as you type. You are not required to use the suggested terms—you can search using any word, and GExplore will find matches containing your search word.
The Tissues and Stages (Genomic Studies) search field refers to data from single-cell RNAseq studies or enrichment analysis of high-throughput studies, where expression in specific tissues is compared to whole animals.
Gene Ontology and Disease Association Search Fields
These search fields also use predefined vocabularies and feature an autosuggest function to help find relevant terms.
Search Fields on the Mutation Search Page
Checkbox: "Do not show deletions affecting more than one gene"
Some deletions are large and affect multiple genes. If your goal is to identify mutations in a single gene, you can use this checkbox to exclude large deletions that affect more than one gene.
Mutation Type
The Mutation Type checkboxes allow you to limit the output to mutations that significantly impact the protein. Nonsense and Deletion mutation types give you more flexibility:
Nonsenses removing greater than x% and Deletions removing greater than x%:
Limits the output to nonsense allele/deletions that truncate the proteins by at least x%. This might be useful to identify putative null alleles by eliminating alleles that only affect the C-terminus of the protein.
Mutation Source (Million Mutation Project, KO Consortium, Other)
The Mutation Source field allows you to filter mutations based on their origin:
- Million Mutation Project: A large number of mutations were identified by random mutagensis followed by whole-genome sequencing, see Thompson et al. (2013).
- KO Consortium: The KO Consortium (Moerman and Barstead (2008)) provides putative null alleles.
- Other Sources: Includes mutations from individual research projects by the C. elegans community.
Search Fields on the Expression Search Pages (Stages, Tissues, Embryos, Species)
Each of the four pages has unique search fields based on the underlying expression database. Details can be found directly on the search pages.
Last updated on Oct 24, 2024
Display Options
General Comments
All result pages now have a consistent format, with a sidebar showing either a summary of the results or various display options or a help section. Data are presented in a flexible table format. Users can export the results as raw text TXT or in CSV format for further local processing.
The "List of proteins/genes found" section contains the list of genes or proteins that meet the search criteria. This list can be copied and used to compare different search results using the Compare tool (refer to the Tools section for details).
Most display options add an extra column to the results table with the relevant data. The names of these options are generally self-explanatory.
Protein Domain Organization
Protein domains, such as SMART or Pfam domains, are displayed as small rectangles containing a unique domain abbreviation. Larger meta-domains, like 7TM_chemorcpt_1, which typically span the entire protein, are represented as larger rectangles. Note that the size of the rectangle does not correspond to the actual size of the domain.
A table of abbreviations is used for selected domains that are found in multiple proteins. SMART/Pfam domains that are not listed in the abbreviation table are shown as gray rectangles with the SMART/Pfam identifier inside. These rectangles link to the corresponding SMART or Pfam entry.
Numbers within the rectangles represent the number of amino acids and indicate parts of the protein that are not assigned to any domain. To improve performance, images representing the domain organization of all proteins were pre-calculated for faster response times.
Gaps between domains that are smaller than 30 amino acids are suppressed, as they likely reflect artificial boundaries of the consensus sequences used to predict domains, which tend to be smaller than the actual domain. For example, an Immunoglobulin (IG) domain is approximately 125 amino acids in size, while the consensus sequence for the SMART IG domain (SM000409) is only 100 amino acids.
On the mutation results page, users can adjust the suppression of gaps to a smaller value for more precise output.
Special Display Options for Mutations
Show gaps > x amino acids:
By default, gaps greater than 30 amino acids are suppressed (as explained above). If a more precise location of the mutation is needed, users can lower this threshold to show smaller gaps between domains.
Special Display Options for Expression Data (Stages, Tissues, Embryo)
Checkboxes: Each of the three expression data sets (stages, tissues, embryo) has a graphic display of expression data for each gene. To provide a complete overview of these data sets, each results page includes checkboxes that allow users to also display the graphs for:
Stage-specific expression graphL2 tissue expression graphEmbryonic tissue expression graph
By selecting these options, users can easily access all three graphical representations, offering a comprehensive view of the gene expression across different stages, tissues, and embryonic development.
Special Display Options for Species Expression Data
Checkboxes: The checkbox 'Homologs (orthogroups)' allows the display of all homologs of the original gene set. Sort the 'Orthogroup' column to have the corresponding homologs in adjacent rows. Rows can also be rearranged by dragging them into a new position.
Last updated on March 23, 2025
Tools
Compare Tool
Compare provides an easy way to find unique and common genes within two sets of genes (two lists of terms of any kind). The input fields accept a list of terms such as the "list of genes/proteins" found on the results pages of GExplore. Names can be separated by commas, semicolons, space or newline characters. The output consists of three lists: the common genes and the unique genes from each of the two input sets.
Convert Tool
The convert input field accepts any combination of C. elegans gene identifiers:
- Locus Name:
nid-1 - Gene Sequence Name:
F54F3.1 - WormBase Gene ID:
WBGene00003738 - Protein Sequence Name:
F54F3.1a - Wormpep ID:
CE18731 - Uniprot ID:
Q93791
Names can be separated by commas, semicolons, space or newline characters. The output consists of a table with all the identifiers for all the genes in the input field. This can be used to standardize identifiers that come from different sources or to convert one set of identifiers into another one.
Last updated on Oct 14, 2024
Table of Domain Abbreviations
Domains are depicted as small rectangles containing a unique domain abbreviation. Meta-domains like 7TM_chemorcpt_1, which typically cover the entire protein, are displayed as larger rectangles. The size of the rectangle does not reflect the actual domain size.
| Abbreviation | Display | Pfam | SMART | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14_3_3 | 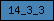 |
PF00244 | SM00101 | 14_3_3 domain |
| 3b-HSD |  |
PF01073 | 3-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/isomerase family | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Sra |  |
PF02117 | Nematode chemoreceptor, Sra | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srab |  |
PF10292 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srab | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srb |  |
PF02175 | Serpentine beta receptor | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srbc |  |
PF10316 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR chemoreceptor Srbc | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Sre |  |
PF03125 | C. elegans Sre G protein-coupled chemoreceptor | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srg |  |
PF02118 | Serpentine gamma receptor, Caenorhabditis species | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srh |  |
PF10318 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srh | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Sri |  |
PF10327 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Sri | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srj |  |
PF10319 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srj | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srr |  |
PF03268 | Domain of unknown function DUF267 | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srsx |  |
PF10320 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srsx | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srt |  |
PF10321 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srt | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Sru |  |
PF10322 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Sru | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srv |  |
PF10323 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srv | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srw |  |
PF10324 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srw | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srx |  |
PF10328 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srx | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srxa |  |
PF03383 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srxa | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Srz |  |
PF10325 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Srz | |
| 7TM_GPCR_Str |  |
PF10326 | Serpentine type 7TM GPCR receptor class Str | |
| AA_perm |  |
PF00324 | amino acid permease | |
| Aa_trans | 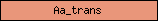 |
PF01490 | amino acid transporter | |
| AAA |  |
PF00004 | SM00382 | AAA ATPase |
| ABC2_m | 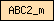 |
PF01061 | ABC-2 type transporter | |
| ABC_transporter |  |
PF00005 | ABC transporter related | |
| ABC_transporter_TM |  |
PF00664 PF06472 | ABC transporter, transmembrane region, type 1 | |
| ABHyd |  |
PF00561 | alpha/beta hydrolase fold | |
| AbHyd3 | 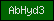 |
PF07859 | alpha/beta hydrolase fold | |
| ACBP |  |
PF00887 | Acyl CoA binding protein | |
| AcCoA_dh |  |
PF00441 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain | |
| actin |  |
PF00022 | SM00268 | Actin/actin-like |
| Acy_dh2 |  |
PF08028 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain | |
| Acy_dh_M |  |
PF02770 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, middle domain | |
| Acy_dh_N |  |
PF02771 | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, N-terminal domain | |
| AcylT |  |
PF00583 | AhpC/TSA family | |
| Acyltransferase |  |
PF01757 | Acyltransferase 3 | |
| AD |  |
PF01421 | Peptidase M12B, ADAM/reprolysin | |
| ADH_N |  |
PF00107 | Zinc-binding dehydrogenase | |
| Ah_perox | 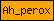 |
PF03098 | Animal haem peroxidase | |
| AhpC |  |
PF00578 | AhpC/TSA family | |
| AKR |  |
PF00248 | Aldo/keto reductase family | |
| Aldedh |  |
PF00171 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family | |
| AMPB | 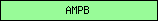 |
PF00501 | AMP-binding enzyme | |
| ANFR |  |
PF01094 | receptor family ligand binding region | |
| Ankyr |  |
PF00023 | SM00248 | Ankyrin repeat |
| APH |  |
PF01636 | Phosphotransferase enzyme family | |
| Apple |  |
PF00024 | SM00223 SM00473 | apple |
| Arm | 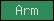 |
PF00514 | SM00185 | armadillo repeat |
| Arre_C |  |
PF02752 | SM01017 | Arrestin (or S-antigen), C-terminal domain |
| Arre_N | 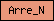 |
PF00339 | Arrestin (or S-antigen), N-terminal domain | |
| Asp |  |
PF00026 | Aspartate protease | |
| AT |  |
PF01821 | SM00104 | Anaphylatoxin/fibulin |
| AT_12 |  |
PF00155 | Aminotransferase class I and II | |
| AT_5 |  |
PF00266 | Aminotransferase class-V | |
| AT_hook | 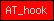 |
PF02178 | SM00384 | DNA binding domain with preference for A/T rich regions |
| B4_1N | 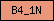 |
PF00373 | SM00295 | Band 4.1, N-terminal |
| BACK | 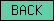 |
PF07707 | SM00875 | BTB And C-terminal Kelch |
| Band_7 |  |
PF01145 | SM00244 | Band 7 protein (found in stomatin) |
| Bestrophin |  |
PF01062 | Bestrophin | |
| bHLH | 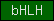 |
PF00010 | SM00353 | Basic helix-loop-helix region |
| BPI2 | 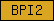 |
PF02886 | SM00329 | BPI/LBP/CETP C-terminal domain |
| Branch |  |
PF02485 | Core-2/I-Branching enzyme | |
| BRCT |  |
PF00533 | SM00292 | BRCT |
| Bromo |  |
PF00439 | SM00297 | Bromodomain |
| BTB |  |
PF00651 | SM00225 | BTB/POZ-like |
| bZIP |  |
PF07716 | SM00338 | Basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor |
| C1 | 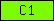 |
PF00130 | SM00109 | Protein kinase C, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol binding |
| C2 | 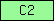 |
PF00168 | SM00239 | C2 calcium-dependent membrane targeting |
| C6 | 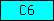 |
PF01681 PF02795 | SM01048 | Protein of unknown function C6 |
| C_AcyT |  |
PF00755 | Choline/Carnitine o-acyltransferase | |
| CA |  |
PF00028 | SM00112 | cadherin |
| Carbesterase_B |  |
PF00135 | Carboxylesterase, type B | |
| Cation_efflux |  |
PF01545 | cation efflux family | |
| CBM | 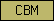 |
PF01607 | SM00494 | Peritrophin-A domain is found in chitin binding proteins |
| CBS |  |
SM00116 | Domain in cystathionine beta-synthase and other proteins | |
| CH | 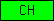 |
PF00307 | SM00033 | Calponin homology domain |
| Chit | 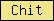 |
SM00636 | Chitinase II | |
| CHK | 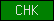 |
SM00587 | ZnF_C4 abd HLH domain containing kinases domain | |
| Chromo | 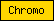 |
PF00385 | SM00298 | Chromo domain |
| CK |  |
SM00041 | Growth factor, cystine knot | |
| CL | 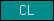 |
PF00059 | SM00034 | C-type lectin |
| Claudin3 |  |
PF06653 | Tight junction protein, Claudin-like | |
| CLC | 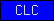 |
PF07062 | claudin homolog | |
| cNMP |  |
SM00100 | Cyclic nucleotide-monophosphate binding domain | |
| COL | 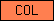 |
PF01391 | collagen | |
| ColN | 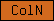 |
PF01484 | SM01088 | N-terminus of cuticular collagens |
| CRIB |  |
PF00786 | SM00285 | PAK-box/P21-Rho-binding |
| CT | 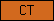 |
PF00100 | SM00241 | Endoglin/CD105 antigen |
| Ctr |  |
PF04145 | Ctr copper transporter family | |
| CtX | 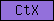 |
PF02363 | C_tripleX; cysteine rich repeat | |
| CUB | 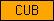 |
PF00431 PF02408 | SM00042 | CUB domain |
| CW |  |
PF08277 | SM00605 | CW domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) |
| CX | 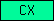 |
PF01705 | CX domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) | |
| CY | 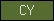 |
PF00031 | SM00043 | Proteinase inhibitor I25, cystatin |
| CYCL | 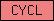 |
PF00134 | SM00385 | domain present in cyclins, TFIIB and Retinoblastoma |
| CysPc |  |
PF00648 | SM00230 | Calpain-like thiol protease family |
| Cyt-b5 | 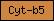 |
PF00173 | Cytochrome b5 | |
| Cytochrome_P450 |  |
PF00067 | Cytochrome P450 | |
| DAO |  |
PF01266 | FAD dependent oxidoreductase | |
| DB | 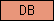 |
PF01682 | DB domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) | |
| DC |  |
SM00289 | DC-domain; Cysteine-rich repeat | |
| DEAD_N |  |
SM00487 | DEAD-like helicase, N-terminal | |
| Death |  |
PF00531 | SM00005 | Death domain |
| DH_SDR |  |
PF00106 | SM00822 | Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase SDR |
| DI | 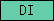 |
PF00200 | SM00050 | disintegrin domain |
| DLH | 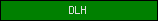 |
PF01738 | Dienelactone hydrolase family | |
| DM | 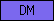 |
PF00751 | SM00301 | Doublesex DNA-binding motif |
| DnaJ |  |
SM00271 | DnaJ molecular chaperone homology domain | |
| DOMON | 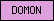 |
PF03351 | SM00664 | DOMON domain |
| DSL |  |
PF01414 | SM00051 | Delta/Serrate/lag-2 (DSL) domain |
| DSRM | 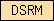 |
PF00035 | SM00358 | Double-stranded RNA binding motif |
| DUF1096 |  |
PF06493 | Domain of unknown function DUF1096 | |
| DUF1114 | 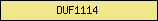 |
PF06542 | Domain of unknown function DUF1114 | |
| DUF1248 |  |
PF06852 | Domain of unknown function DUF1248 | |
| DUF1258 |  |
PF06869 | Domain of unknown function DUF1258 | |
| DUF1261 |  |
PF06879 | Domain of unknown function DUF1261 | |
| DUF1265 |  |
PF06887 | Domain of unknown function DUF1265 | |
| DUF1280 | 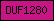 |
PF06918 | Domain of unknown function DUF1280 | |
| DUF13 |  |
PF01482 | Domain of unknown function DUF13 | |
| DUF130 |  |
PF02343 | Domain of unknown function DUF130 | |
| DUF148 | 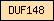 |
PF02520 | Domain of unknown function DUF148 | |
| DUF1605 |  |
PF07717 | Domain of unknown function DUF1605 | |
| DUF1647 |  |
PF07801 | Domain of unknown function 1647 | |
| DUF1679 |  |
PF07914 | Domain of unknown function DUF1679 | |
| DUF19 |  |
PF01579 PF03236 | Domain of unknown function DUF19 | |
| DUF227 | 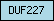 |
PF02958 | Domain of unknown function DUF227 | |
| DUF229 |  |
PF02995 | Domain of unknown function DUF229 | |
| DUF23 |  |
PF01697 | Domain of unknown function DUF23 | |
| DUF236 |  |
PF03057 | Domain of unknown function DUF236 | |
| DUF2650 |  |
PF10853 | Domain of unknown function DUF2650 | |
| DUF268 |  |
PF03269 | Domain of unknown function DUF268 | |
| DUF271 | 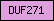 |
PF03407 | Domain of unknown function DUF271 | |
| DUF272 | 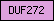 |
PF03312 | Domain of unknown function DUF272 | |
| DUF273 |  |
PF03314 | Domain of unknown function DUF273 | |
| DUF274 |  |
PF03409 | Domain of unknown function DUF274 | |
| DUF281 |  |
PF03436 | Domain of unknown function DUF281 | |
| DUF282 | 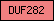 |
PF03380 | Domain of unknown function DUF282 | |
| DUF288 |  |
PF03385 | Domain of unknown function DUF288 | |
| DUF316 |  |
PF03761 | Domain of unknown function DUF316 | |
| DUF3557 |  |
PF12078 | Domain of unknown function DUF3557 | |
| DUF38 |  |
PF01827 | Domain of unknown function DUF38 | |
| DUF595 |  |
PF04590 | Domain of unknown function DUF595 | |
| DUF621 |  |
PF04789 | Domain of unknown function DUF621, putative G-protein coupled receptor | |
| DUF644 |  |
PF04870 | Domain of unknown function DUF644 | |
| DUF672 |  |
PF05050 | Domain of unknown function DUF672 | |
| DUF684 | 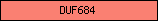 |
PF05075 | Domain of unknown function DUF684 | |
| DUF780 | 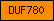 |
PF05611 | Domain of unknown function DUF780 | |
| DUF870 | 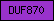 |
PF05912 | Domain of unknown function DUF870 | |
| DUF976 |  |
PF06162 | Domain of unknown function DUF976 | |
| DUF_CC | 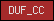 |
PF04942 | Domian of unknown function, DUF-CC | |
| E1E2ATP |  |
PF00122 | proton ATPase | |
| EamA |  |
PF00892 | EamA-like transporter family | |
| EB | 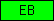 |
PF01683 | EB-domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) | |
| ECH |  |
PF00378 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family | |
| EF-Tu | 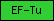 |
PF00009 | GTP-binding elongation factor family, EF-Tu/EF-1A subfamily | |
| EF-Tu2 |  |
PF03144 | Elongation factor Tu domain 2 | |
| EF_hand |  |
PF00036 | SM00054 | Calcium-binding EF-hand |
| EGF |  |
PF00008 PF07974 PF07645 | SM00001 SM00179 SM00181 | EGF module |
| Epi |  |
PF01370 | NAD dependent epimerase/dehydratase family | |
| ET | 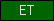 |
PF01684 | Domain of unknown function ET | |
| Ets |  |
PF00178 | SM00413 | Ets domain |
| EXOIII |  |
SM00479 | exonuclease domain in DNA-polymerase alpha and epsilon chain, ribonuclease T and other exonucleases | |
| F5_8C | 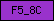 |
PF00754 | SM00231 | Coagulation factor 5/8 type, C-terminal |
| FADB2 |  |
PF00890 | FAD binding domain | |
| FARP |  |
PF01581 | FMRFamide related peptide family | |
| Fba_2 |  |
PF07735 | F-box associated type 2 | |
| Fbox |  |
PF00646 | SM00256 | Fbox |
| FeoB_N |  |
PF02421 | Ferrous iron transport protein B | |
| FERM_C |  |
PF09380 | FERM C-terminal PH-like domain | |
| FG | 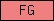 |
PF00147 | SM00186 | Fibrinogen, alpha/beta/gamma chain, C-terminal globular |
| FHA | 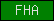 |
PF00498 | SM00240 | Forkhead-associated |
| FN3 |  |
PF00041 | SM00060 | Fibronectin, type III-like fold |
| FolN | 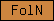 |
PF09120 PF09289 | SM00274 | Follistatin-like, N-terminal |
| Fork_Hd |  |
PF00250 | SM00339 | Fork head transcription factor |
| Fringe |  |
PF02434 | Fringe-like | |
| FU |  |
SM00261 | furin repeat | |
| Fukutin |  |
PF06828 | Fukutin-related | |
| FZ | 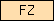 |
PF01392 | SM00063 | Frizzled cysteine-rich domain |
| G_alpha |  |
PF00503 | SM00275 | Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G-protein), alpha subunit |
| G_patch |  |
PF01585 | SM00443 | glycine rich nucleic binding domain |
| Gal_T |  |
PF01762 | Galactosyltransferase | |
| Gcyc | 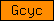 |
PF00211 | SM00044 | guanylate cyclase |
| GL |  |
PF00337 | SM00276 SM00908 | Galectin, galactose-binding lectin |
| Globin |  |
PF00042 | Globin-like | |
| Glycoside_hydrolase | 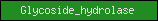 |
PF00933 | Glycoside hydrolase, catalytic core | |
| GlyT |  |
PF01531 | Glycosyl transferase family 11 | |
| GlyT28_C |  |
PF04101 | Glycosyltransferase family 28 C-terminal domain | |
| GlyTr2 | 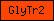 |
PF00535 | Glycosyl transferase family 2 | |
| GPCR_Rhodopsin |  |
PF00001 | GPCR, rhodopsin-like superfamily | |
| GPCR_secretin |  |
PF00002 | GPCR, family 2, secretin-like | |
| GPS |  |
PF01825 | SM00303 | GPS domain |
| GR |  |
PF00462 | Glutaredoxin | |
| Gra6 |  |
PF05084 | Gra6 domain | |
| Gran | 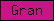 |
PF00396 | SM00277 | Granulin |
| Grd |  |
PF04155 | ground domain | |
| GST_N |  |
PF02798 | Glutathione S-transferase, N-terminal domain | |
| GTPase | 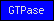 |
PF00025 PF00071 PF08477 | SM00010 SM00173 SM00174 SM00175 SM00176 SM00177 SM00178 | small GTPases (all subfamilies, Ras, Ran, Rac, etc...) |
| H2A | 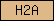 |
SM00414 | histone H2A | |
| H2B |  |
SM00427 | histone H2B | |
| H3 |  |
SM00428 | histone H3 | |
| H4 | 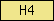 |
SM00417 | histone H4 | |
| HA2 |  |
PF04408 | SM00847 | Helicase associated domain (HA2) |
| HEAT | 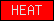 |
PF02985 | HEAT | |
| Helic_C | 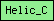 |
PF00271 | SM00490 | DNA/RNA helicase, C-terminal |
| HintC |  |
SM00305 | Hint (Hedgehog/Intein) domain C-terminal region | |
| HintN |  |
PF01079 | SM00306 | Hint (Hedgehog/Intein) domain N-terminal region |
| HisPhos2 |  |
PF00328 | Histidine phosphatase superfamily (branch 2) | |
| Histone |  |
PF00125 PF00538 | SM00526 | Histone fold |
| HMG |  |
PF00505 | SM00398 | High mobility group box, HMG1/HMG2, subgroup |
| HOM |  |
PF00046 | SM00389 | homeobox |
| HSP20 |  |
PF00011 | HSP20-like chaperone | |
| Hsp70 |  |
PF00012 | Heat shock protein 70 | |
| HX | 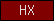 |
PF00045 | SM00120 | hemopexin |
| Hydrol |  |
PF00702 | haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase | |
| I29 | 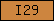 |
SM00848 | Cathepsin propeptide inhibitor domain (I29) | |
| IBR | 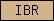 |
PF01485 | SM00647 | In Between Ring fingers |
| IFP | 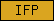 |
PF00038 | Intermediate filament protein | |
| IG | 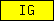 |
PF07654 PF07679 PF07686 PF00047 PF08205 | SM00406 SM00407 SM00408 SM00409 SM00410 | immunoglobulin domain |
| Innexin |  |
PF00876 | Innexin | |
| Insulin |  |
PF03488 | SM00078 | Nematode insulin-related peptide, beta type |
| Ion_glu_rcpt |  |
PF00060 | Ionotropic glutamate receptor | |
| Ion_tr | 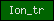 |
PF00520 | four TM helices additionally present in many channels | |
| IQ | 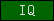 |
PF00612 | SM00015 | Short calmodulin-binding motif containing conserved Ile and Gln residues |
| JmjC |  |
PF02373 PF08007 | SM00558 | A domain family that is part of the cupin metalloenzyme superfamily |
| K_chan_2pore | 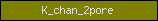 |
PF07885 | Potassium channel, two pore-domain | |
| K_chan_volt |  |
PF02214 | Potassium channel, voltage dependent, Kv, tetramerisation | |
| Kelch | 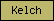 |
PF01344 PF07646 | SM00612 | Kelch repeat type 1 |
| KH | 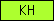 |
PF00013 | SM00322 | K Homology |
| KIN |  |
PF00069 PF07714 | SM00219 SM00220 SM00221 | protein kinase |
| Kin_Ct |  |
SM00133 | AGC-kinase, C-terminal | |
| Kinesin_motor |  |
PF00225 | SM00129 | Kinesin, motor region |
| KR | 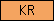 |
PF00051 | SM00130 | kringle |
| KU | 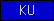 |
PF00014 | SM00131 | Kunitz domain/Proteinase inhibitor I2 |
| KZ | 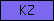 |
PF00050 PF07648 | SM00280 | Proteinase inhibitor I1, Kazal |
| LA | 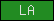 |
PF00057 | SM00192 | Low density lipoprotein-receptor, class A domain |
| Lactam_B |  |
PF00753 | SM00849 | Metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily |
| LamB |  |
PF00052 | SM00281 | Laminin B domain |
| LE | 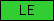 |
PF00053 | SM00180 | laminin EGF-like domain |
| LG |  |
PF00054 PF02210 | SM00210 SM00282 | laminin G domain |
| LGC-GluB | 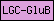 |
PF10613 | SM00918 | Ligated ion channel L-glutamate- and glycine-binding site |
| LIM |  |
PF00412 | SM00132 | LIM domain |
| Lin-8 |  |
PF03353 | Ras-mediated vulval-induction antagonist | |
| Lip_2 |  |
PF01674 | Lipase (class 2) | |
| Lip_3 |  |
PF01764 | Lipase (class 3) | |
| Lip_G |  |
PF00657 | GDSL-like Lipase/Acylhydrolase | |
| LisH |  |
SM00667 | Lissencephaly type-1-like homology motif | |
| LITAF |  |
SM00714 | Possible membrane-associated motif in LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha factor | |
| LN |  |
PF00055 | SM00136 | laminin, N-terminal domain |
| LRR |  |
PF00560 | SM00369 SM00370 SM00368 | leucine-rich repeat |
| LRRc |  |
PF01463 | SM00082 | leucine-rich repeat, C-terminal |
| LRRn |  |
PF01462 | SM00013 | leucine-rich repeat, N-terminal |
| LTD |  |
PF00932 | Lamin Tail Domain | |
| LY |  |
PF00058 | SM00135 | Low-density lipoprotein receptor, YWTD repeat |
| LZ |  |
PF04916 | laminin A domain | |
| MAM |  |
PF00629 | SM00137 | MAM domain |
| MATH | 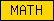 |
PF00917 | SM00061 | MATH domain |
| MBOAT |  |
PF03062 | membrane-bound o-acyltransferase | |
| MD |  |
SM00604 | MD domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) | |
| MFP2b |  |
PF12150 | Cytosolic motility protein | |
| MFS_1 |  |
PF07690 | Major facilitator superfamily MFS-1 | |
| Mitoch_carrier |  |
PF00153 | Mitochondrial substrate carrier | |
| MMR |  |
PF01926 | 50S ribosome-binding GTPase | |
| MP |  |
SM00235 | metalloprotease (covers all, should be replaced in display by the appropriate subfamily, e.g. PepM12) | |
| MreB |  |
PF06723 | MreB/Mbl protein | |
| MSP |  |
PF00635 | Major sperm protein | |
| MSP4 |  |
PF07993 | Male sterility protein | |
| MT_11 |  |
PF08241 | Methyltransferase domain | |
| MT_12 | 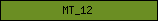 |
PF08242 | Methyltransferase domain | |
| MTS |  |
PF05175 | Methyltransferase small domain | |
| MYND | 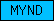 |
PF01753 | MYND finger | |
| Myosin_head |  |
PF00063 | SM00242 | Myosin head, motor region |
| Myosin_tail | 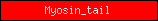 |
PF01576 | Myosin tail | |
| N1 | 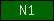 |
PF06119 | SM00539 | nidogen, N-terminal domain |
| Na_Ca_ex |  |
PF01699 | sodium/calcium exchanger protein | |
| Na_chan_AS | 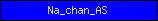 |
PF00858 | Na+ channel, amiloride-sensitive | |
| Na_diCO_symport | 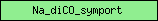 |
PF00375 | Sodium:dicarboxylate symporter | |
| Na_H_ex | 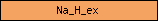 |
PF00999 | sodium/hydrogen exchanger family | |
| NC10 |  |
PF06482 | endostatin | |
| Neuro_channel_lgbd |  |
PF02931 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel | |
| Neuro_channel_tm |  |
PF02932 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel transmembrane region | |
| NhrLig |  |
PF00104 | SM00430 | Nuclear hormone receptor, ligand-binding |
| NRF |  |
SM00703 | N-terminal domain in C. elegans NRF-6 (Nose Resistant to Fluoxetine-4) and NDG-4 (resistant to nordihydroguaiaretic acid-4) | |
| Nuclease |  |
PF00929 | Polynucleotidyl transferase, Ribonuclease H fold | |
| NucST |  |
PF04142 | Nucleotide-sugar transporter | |
| NUDIX |  |
PF00293 | NUDIX domain | |
| P-Diest |  |
PF01663 | Type I phosphodiesterase / nucleotide pyrophosphatase | |
| P_ATP_C |  |
PF00689 | Cation transporting ATPase, C-terminus | |
| P_ATP_N | 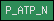 |
SM00831 | Cation transporter/ATPase, N-terminus | |
| P_Propr |  |
PF01483 | Proprotein convertase P-domain | |
| PALP | 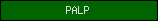 |
PF00291 | Pyridoxal-phosphate dependent enzyme | |
| Patatin |  |
PF01734 | Patatin-like phospholipase | |
| Patched |  |
PF02460 | Patched | |
| PAW | 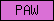 |
PF04721 | SM00613 | Protein of unknown function PAW |
| PAX |  |
PF00292 | SM00351 | Paired box protein, N-terminal |
| PAZ |  |
PF02170 | SM00949 | Argonaute and Dicer protein, PAZ |
| PBPb |  |
PF00497 | SM00062 | Bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding proteins |
| PBPe |  |
SM00079 | Eukaryotic homologues of bacterial periplasmic substrate binding proteins | |
| PDZ |  |
PF00595 | SM00228 | PDZ domain |
| PepC1 |  |
SM00645 | Peptidase family C1 | |
| PepM1 |  |
PF01433 | Peptidase family M1 | |
| PepM10 |  |
PF00413 | matrixin and adamalysin; Peptidase M10A and M12B | |
| PepM12 |  |
PF01400 | astacin, peptidase M12A | |
| PepM13 |  |
PF01431 | neprilysin | |
| PepM13_N |  |
PF05649 | Peptidase family M13 | |
| PepM14 |  |
PF00246 | SM00631 | Peptidase M14, carboxypeptidase A |
| PepM16 |  |
PF00675 | Insulinase (Peptidase family M16) | |
| PepM16_C | 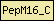 |
PF05193 | Peptidase M16 inactive domain | |
| PepS1 |  |
PF00089 | SM00020 | Peptidase S1 and S6, chymotrypsin/Hap; Peptidase, trypsin-like serine and cysteine |
| PepS10 |  |
PF00450 | Peptidase family S10 | |
| PepS28 |  |
PF05577 | Serine carboxypeptidase S28 | |
| PepS8 |  |
PF00082 | Peptidase S8 and S53, subtilisin, kexin, sedolisin | |
| PepS9 |  |
PF00326 | Prolyl oligopeptidase family | |
| Pfam |  |
all other Pfam domains | ||
| PGAM |  |
PF00300 | SM00855 | Phosphoglycerate mutase family |
| PH |  |
PF00169 PF00568 PF00640 | SM00233 SM00461 SM00462 | Pleckstrin-homology domain |
| Phox |  |
PF00787 | SM00312 | Phox-like |
| Phtase |  |
PF00149 | SM00156 | phosphoprotein phosphatase |
| PI3K |  |
PF00794 PF00454 | SM00144 SM00146 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PINT |  |
PF01399 | SM00088 | motif in proteasome subunits, Int-6, Nip-1 and TRIP-15 |
| Piwi |  |
PF02171 | SM00950 | Stem cell self-renewal protein Piwi |
| PKD |  |
PF08016 | Polycystin cation channel | |
| PlsC |  |
SM00563 | Phosphate acyltransferases | |
| Pmp3 |  |
PF01679 | proteolipid membrane potential modulator | |
| Polys2 |  |
PF02719 | Polysaccharide biosynthesis protein | |
| POU |  |
PF00157 | SM00352 | POU domain |
| PP2Cc |  |
PF00481 PF07228 | SM00331 SM00332 | 1) Sigma factor PP2C-like phosphatases, 2) Serine/threonine phosphatases, family 2C, catalytic domain |
| Prefoldin |  |
PF01920 | Prefoldin | |
| PrmA | 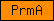 |
PF06325 | Ribosomal protein L11 methyltransferase (PrmA) | |
| Pro_iso |  |
PF00160 | Cyclophilin type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase/CLD | |
| Protea |  |
PF00227 | Proteasome subunit | |
| PTP | 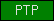 |
PF00102 PF00782 | SM00012 SM00194 SM00195 SM00404 | protein-tyrosine phosphatase |
| Ptre |  |
PF00088 | SM00018 | P-type trefoil domain |
| PUF |  |
PF00806 | SM00025 | Pumilio-like repeats |
| Pyr_deC | 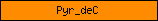 |
PF00282 | Pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylase conserved domain | |
| PyrR2 |  |
PF07992 | Pyridine nucleotide-disulphide oxidoreductase | |
| Ras_as |  |
PF00788 | SM00314 | ras-association domain |
| RasGAP |  |
PF00616 | SM00323 | ras GTPase activating protein |
| RcpL | 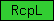 |
PF01030 | EGF receptor, L domain | |
| Redox |  |
PF08534 | Redoxin | |
| RGS |  |
PF00615 | SM00315 | Regulator of G protein signalling |
| RHOD | 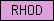 |
PF00581 | SM00450 | Rhodanese Homology Domain |
| RhoGAP | 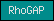 |
PF00620 | SM00324 | RhoGAP domain |
| RhoGEF |  |
PF00621 | SM00325 | RhoGEF domain |
| Rhomb |  |
PF01694 | Rhomboid protease | |
| RICIN | 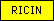 |
SM00458 | Ricin-type beta-trefoil | |
| RmSB |  |
PF04321 | RmlD substrate binding domain | |
| RRM |  |
PF00076 | SM00360 SM00361 SM00362 | RNA recognition motif, RNP-1 |
| S1 |  |
PF00575 | SM00316 | Ribosomal protein S1-like RNA-binding domain |
| SAM |  |
PF00536 PF07647 | SM00454 | Sterile alpha motif homology |
| SANT |  |
PF00249 | SM00717 | SANT SWI3, ADA2, N-CoR and TFIIIB'' DNA-binding domains |
| SapB |  |
SM00741 | Saposin B | |
| SCPlike | 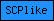 |
PF00188 | SCP-like extracellular | |
| SEA |  |
PF01390 | SM00200 | SEA domain |
| SEC14 |  |
PF00650 | SM00516 | Domain in homologues of a S. cerevisiae phosphatidylinositol transfer protein (Sec14p) |
| SERPIN |  |
PF00079 | SM00093 | SERine Proteinase Inhibitors |
| SET |  |
PF00856 | SM00317 | SET domain |
| SH2 | 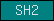 |
PF00017 | SM00252 | SH2 domain |
| SH3 |  |
PF00018 | SM00326 | SH3 domain |
| ShK |  |
PF01549 | SM00254 | Metridin-like ShK toxin |
| Skp1 |  |
SM00512 | Found in Skp1 protein family | |
| Sm |  |
PF01423 | SM00651 | snRNP Sm proteins |
| SM |  |
PF01437 | SM00423 | semaphorin/plexin domain |
| SMART | 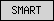 |
all other SMART domains | ||
| SNF | 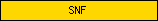 |
PF00209 | sodium neurotransmitter symporter | |
| SNF2_N |  |
PF00176 | SNF2-related | |
| Snf7 |  |
PF03357 | Snf7 | |
| SP | 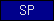 |
signal peptide | ||
| Spec | 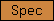 |
PF00435 | SM00150 | spectrin repeat |
| SPK |  |
PF04435 | SM00583 | SPK is a domain of unknown function found in SET and PHD domain containing proteins |
| SPRY | 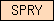 |
PF00622 | SM00449 | Domain in SPla and the RYanodine Receptor. |
| SR |  |
PF00530 | SM00202 | Speract/scavenger receptor |
| Ster-S |  |
PF12349 | Sterol-sensing domain of SREBP cleavage-activation | |
| Sugar_tr |  |
PF00083 | sugar transporter | |
| Sushi | 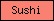 |
PF00084 | SM00032 | Sushi/SCR/CCP domain |
| SynN | 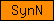 |
SM00503 | Syntaxin N-terminal domain | |
| T1 |  |
PF00090 | SM00209 | Thrombospondin, type I |
| T_Box | 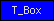 |
PF00907 | SM00425 | Transcription factor, T-box |
| TBC | 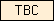 |
PF00566 | SM00164 | Domain in Tre-2, BUB2p, and Cdc16p. Probable Rab-GAPs. |
| TCP1 | 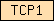 |
PF00118 | HSP60 | |
| Tetraspanin |  |
PF00335 | tetraspanin | |
| TGFb |  |
PF00019 | SM00204 | TGF beta domain |
| TIL | 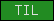 |
PF01826 | prot. Inhibitor domain | |
| TM |  |
transmembrane domain | ||
| TPR | 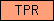 |
PF00515 PF07719 | SM00028 | Tetratricopeptide region |
| TPT | 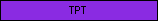 |
PF03151 | Triose-phosphate Transporter family | |
| Transthyr_rel | 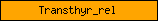 |
PF01060 | Transthyretin-like | |
| Tro_My | 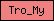 |
PF00261 | Tropomyosin | |
| tSNARE |  |
SM00397 | helical region found in SNAREs | |
| Tubulin_Cterm | 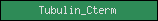 |
PF03953 | SM00865 | Tubulin/FtsZ, C-terminal |
| Tubulin_GTPase |  |
PF00091 | SM00864 | Tubulin/FtsZ, GTPase |
| TY |  |
PF00086 | SM00211 | Thyroglobulin type-1 domain |
| UAA |  |
PF08449 | UAA transporter family | |
| Ub_MT | 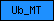 |
PF01209 | ubiE/COQ5 methyltransferase family | |
| UBA | 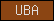 |
PF00627 | SM00165 | Ubiquitin associated domain |
| UBCc |  |
SM00212 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2, catalytic domain | |
| Ubiq |  |
PF00240 | SM00213 | Ubiquitin |
| UBQ_conjugat_E2 |  |
PF00179 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme/RWD-like | |
| UCH |  |
PF00443 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase | |
| UDP_gluc_trans |  |
PF00201 | UDP-glucuronosyl/UDP-glucosyltransferase | |
| UL | 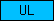 |
PF02140 | D-galactoside lectin | |
| UNC-93 | 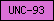 |
PF05978 | Ion channel regulatory protein UNC-93 | |
| V5_TPX | 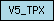 |
SM00198 | Allergen V5/Tpx-1 related | |
| VA |  |
PF00092 | SM00327 | von Willebrand factor, type A domain |
| VC | 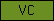 |
PF00093 | SM00214 SM00215 | von Willebrand factor, type C domain |
| VD |  |
PF00094 | SM00216 | von Willebrand factor, type D domain |
| Vincul |  |
PF01044 | Vinculin/alpha-catenin | |
| VOMI | 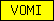 |
PF03762 | Vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VOMI) | |
| WA |  |
PF00095 | SM00217 | Whey acidic protein, 4-disulphide core |
| WD40 |  |
PF00400 | SM00320 | WD40/YVTN repeat |
| Wilms |  |
PF02165 | Wilm's tumour protein | |
| WSN | 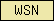 |
PF02206 | SM00453 | WSN domain (found in nematodes only so far ...) |
| WW |  |
PF00397 | SM00456 | WW/Rsp5/WWP |
| Zip |  |
PF02535 | zinc transporter | |
| Znf | 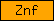 |
PF01428 PF01529 PF02135 PF01363 PF00643 PF00569 PF00642 PF00320 PF00105 PF00641 PF00098 PF00628 PF00096 | SM00064 SM00154 SM00184 SM00249 SM00251 SM00291 SM00336 SM00343 SM0352 SM00355 SM00356 SM00399 SM00401 SM00451 SM00547 SM00551 SM00744 | zinc finger |
| ZU5 | 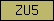 |
PF00791 | SM00218 | ZU5 domain |
Last updated on Oct 14, 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
I hope you can find an answer to your question here. If not - after you have made a serious attempt to figure it out by yourself - you can send an email to H. Hutter.
General Questions
To learn about the latest features and updates in each GExplore release, visit the What's new? section on our Help page.
No, but you can paste even a large list of genes (I tested up to 5000) into the Gene Name search field. Simply generate a comma-delimited list of your favourite genes and paste them into the Gene Name search field.
You can export the results as CSV or TXT files and save them for further processing.
However, The result of a search essentially is a list of genes fullfilling the search condition(s). This list of genes is always on the output page (in the search results sidebar). You can copy it from there and save it on your computer - or paste it into the Gene Name search field for combinatorial searches.
Domain Search and Display
Find the SMART or Pfam identifier of your domain of interest and use it in the Domain search field.
If you care about certain subgroups, you can always use the corresponding SMART or Pfam identifiers in your search. The domain will still be displayed as generic 'Znf' ('KIN', 'GTPase'). There are two reasons for 'collapsing' sometimes large numbers of interpro domains into a single abbreviation. First, this interface is aimed at the 'big picture' (actively ignoring subtle subdivisions) and second, SMART or Pfam domains sometimes do not have the discriminatory power to distinguish subgroups (EGF and IG are typical examples). However, currently some groups of domains might be collapsed too generously. If you are an expert in the field and can suggest a subdivision, please contact Dr. Harald Hutter.
Try TM in the Domain Pattern field. Explanation: Signal peptides have a hydrophobic core, which triggers a hit with algorithms looking for hydrophobic stretches of amino acids to predict transmembrane domains. While searches in the Protein Domain field operate on the 'raw' domain annotations, searches in the Domain Pattern field operate on the domain pattern as you see it in the ouput, i.e. after the 'display rules' have been applied - and one of them suppresses display of transmembrane domains overlapping signal peptides.
Yes, all proteins not having any SMART or Pfam annotation are tagged with 'no_domain'. You can enter this in the Protein Domain search field to retrieve them. Note that signal peptides and transmembrane domains are not considered 'domains' here. If you want proteins that have neither signal sequene, nor transmembrane domain nor any known domain, use 'no_domain not (SP or TM)' in the Protein Domain search field (there are surprisignly few). Note also that you cannot use 'no_domain' as part of a search pattern in the Domain Pattern field. However, since entries in the Protein Domain search field and the Domain Pattern field and effectively combined as logical 'AND' search, you can get all single pass transmembrane domain proteins with no known protein domains by searching for 'no_domain' in the Protein Domain field and 'TM and no more TM' in the Domain Pattern field.
Text Searches and Boolean Logic in Searches
body wall muscle AND neuron in the expression search field and got an error message. Why?
The short answer is, you cannot use multi-word search terms, because SPACE is used to separate search terms. You will not get an error message from just using 'body wall muscle', because it is translated into 'body OR wall OR muscle' - probably not what you wanted. As a work-around for the example above, you could use the following search strategy: search for body AND wall AND muscle, copy the list of genes from the output page, paste it into the Gene Name field of a new search page and search for neuron.
The autosuggestion feature helps you find the correct terms quickly by providing a list of suggestions as you type in input fields such as Protein Domains or Gene Ontology Term. You can navigate through the suggestions using the Up and Down arrow keys. To select a suggestion, press the Enter key. If you want to dismiss the suggestions list, press the Escape key. If the term you enter does not match any available suggestions, the message "No suggestions found" will be displayed. The function recognizes the , separator and will offer suggestions again for a second search term after you entered the separator. Note that the separator for the GO term field is;, since GO terms can contains commas.
Result Page Interface Features
Yes, you can hide the sidebar on the results page to get more space for the table. When the sidebar is open, a vertical line appears next to the active sidebar icon. To collapse the sidebar, simply click on the active icon. This will provide a more expansive view of the results table. If you click on a different sidebar icon while the sidebar is open, it will switch the content to reflect the new sidebar option you selected.
Sidebar Feature
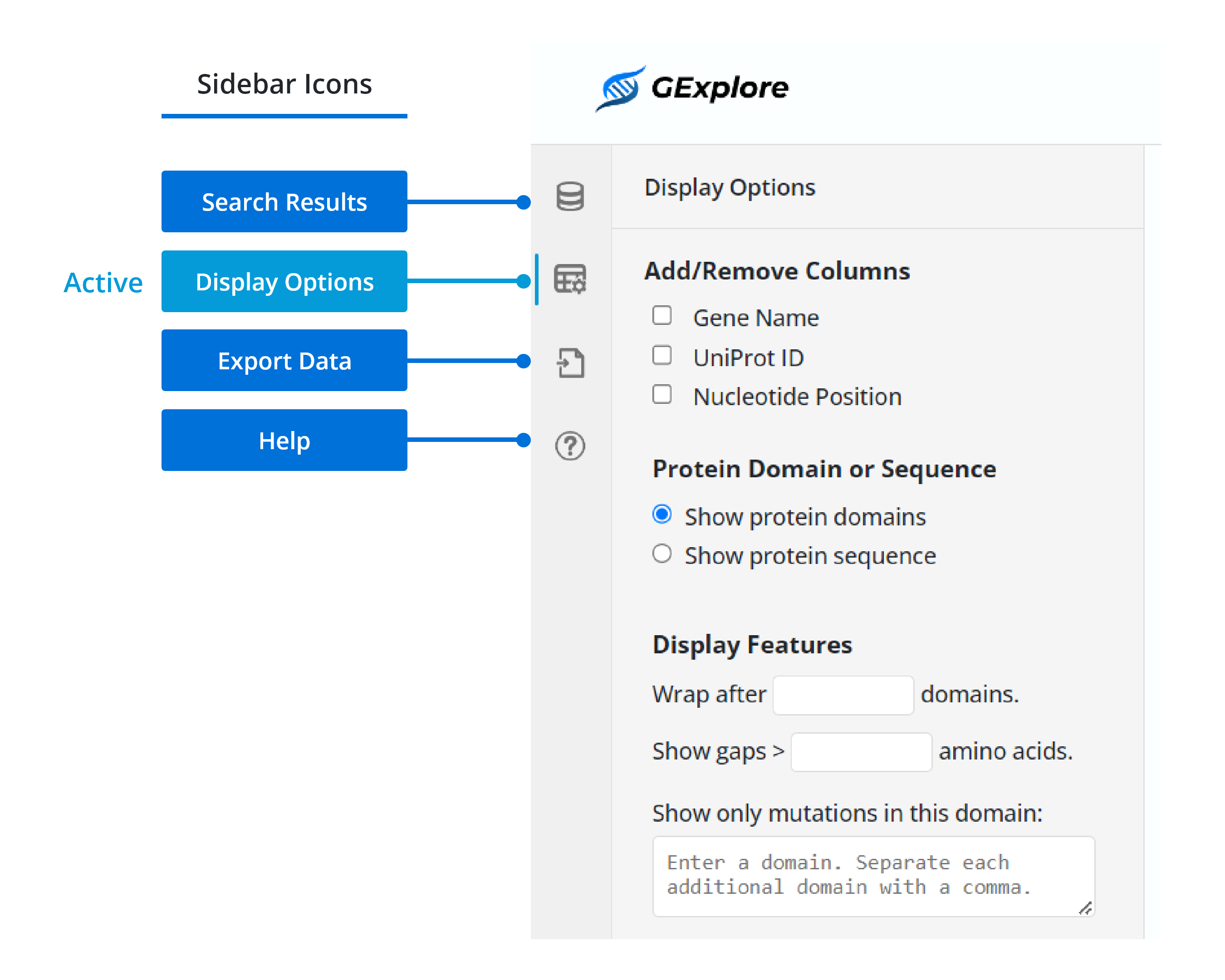
There are three possible reasons: 1. only certain columns can be used for sorting (e.g. the domain organization column does not sort). 2. The output has more than 1000 genes, in which case this functionality is not available (it would be so slow, you wouldn't want to wait). 3. This requires that javascripts are enabled in your browser. Check your browser manual in this case to activate javascript.
Turning off the domain display (domain organization column) will turn off the row-drag functionality. It's main purpose is to allow you to drag proteins around to maybe group those with similar domain organization.
If you uncheck a gene and click 'Update Display' the unchecked gene will be removed from the display. You an use this to manually fine-tune the output and maybe eliminate false positives from a domain search or certain genes you are not interested in before continuing with the analysis. You can use the 'Back' button of your browser to 'undo' this quickly.
Last updated on Oct 14, 2024
Download
If you want to generate a local copy of the GExplore gene and mutation databases you can find instructions and Perl scripts for data download from Wormbase and data processing in this file.
